Institution
Graduate School of Techno Design, Kookmin University
Paper Author
Min Suk Kang
Keyword
Car Interaction, Gesture, Car Interface
Award Title
Outstanding Graduate Thesis Award
[연구 프로세스]
STEP 5
Proposing Possibilities
for the Utilization
of Gestures
STEP 1
Defining Gesture
Interaction Methods
in Vehicles
Conclusion
STEP 2
First User Research
Second User Research
STEP 3
Expert Evaluation >
Final Gesture Extraction
STEP 4
User & Expert FGI >
Gesture Design
for Functional Control
A Study on the Design of Gesture Interaction in Automobiles >
ABSTRACT
This study aims to discover convenient and efficient gestures for controlling functions within a vehicle, with a specific focus on designing gestures for certain functions (radio, audio, heater, and air conditioning) that are not directly related to driving. To accomplish this, I limited the use of gestures to the steering wheel and the center console. Throughout this study, I focused on utilizing gestures specifically within these two areas of the vehicle.
Through user surveys, a variety of useful gestures were uncovered. Subsequently, a final set of gestures, as identified in the surveys, was utilized for expert group interviews to propose gesture designs suitable for operating these functions. The research ultimately serves as a foundation for exploring gesture interaction design environments in vehicles, contributing to driver safety by promoting forward attention and reducing distraction. Additionally, it presents a proposal for new sensory interactions for drivers, incorporating the insights gathered from this study. The aim is to guide future research into gesture interaction design environments for vehicles, utilizing this study as foundational material.
This paper aims to investigate suitable gestures for intuitive and efficient interaction within a vehicle, and to construct a corresponding set of gestures based on the findings.
Additionally, it aims to propose the feasibility of gesture utilization by designing gestures for functions (audio, radio, air conditioning, heater) unrelated to driving, building upon the identified gestures.
Ultimately, it serves as foundational material for researching a gesture design environment suitable for reducing forward distraction and enhancing driver attention during driving for safety. Additionally, it proposes a new emotional interaction for drivers.

Research Objective of Motion-Based Gesture Design
Wheel
Left
Button
Decrease

Right
Decrease
Increase
Left
Right
Decrease
Increase
Increase
Up
Down
조작방식
단위
라디오
오디오
히터
에어컨
Unit-Specific Adjustment Examples
Direction
Operation
Method
Radio
Audio
Heater
에어컨
Wheel
Left
Temperature
Decrease
Temperature
Decrease
Volume Decrease
Volume Decrease
Intensity Decrease
Intensity Decrease
Channel
(Frequency Decrease)
Right
Volume Increase
Channel
(Frequency Increase)
Volume Increase
Intensity Increase
Temperature
Increase
Intensity Increase
Temperature
Increase
Button
Up
Volume Increase
Channel
(Frequency Increase)
Volume Increase
Intensity Increase
Temperature
Increase
Intensity Increase
Temperature
Increase
Down
Volume Decrease
Channel
(Frequency Decrease)
Volume Decrease
Track Decrease
(Previous Track)
Intensity Decrease
Temperature
Decrease
Intensity Decrease
Temperature
Decrease
Left
Channel
(Frequency Decrease)
Right
Channel
(Frequency Increase)
Track Increase
(Next Track)
Track Decrease
(Previous Track)
Track Increase
(Next Track)
Track Decrease
(Previous Track)
Track Increase
(Next Track)
Intensity Decrease
Intensity Increase
Intensity Increase
Intensity Decrease

Identifying Basic Control Units and Operational Models
I have identified the basic operation methods and extracted control units for the applied functions (radio, audio, air conditioner, heater).
[Basic Control Units]
[Manipulation Model]
Wheel Gesture
One Hand Space Gesture
Definition of Gesture Interaction Method
Two methods have been defined for operating functions in a vehicle:
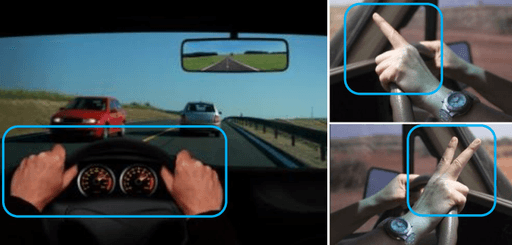
Wheel Gesture:
The driver, with both hands on the steering wheel while driving, manipulates non-driving-related functions. This gesture is performed without using the screen, distinguishing it from GUI-based interactions involving menus or icons on the screen.
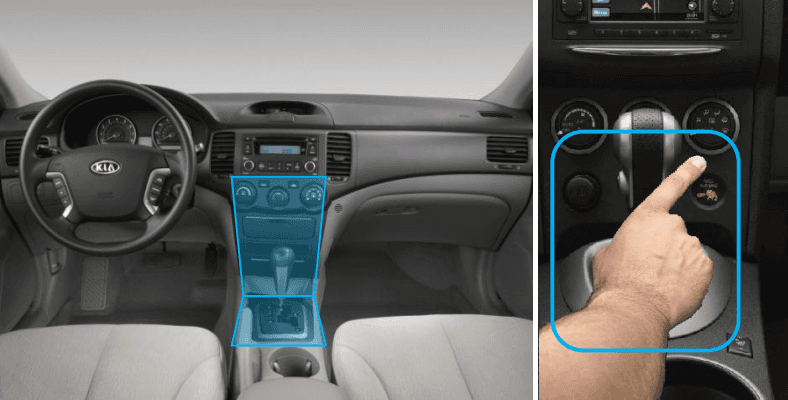
One Hand Space Gesture:
When wanting to operate non-driving-related functions in the vicinity of the Center Fascia or above the gear lever using one hand, the driver utilizes the One Hand Space Gesture. Similar to the first method, this gesture doesn't involve interacting with menus or icons on a GUI-based screen but emphasizes screen-free gesture interaction.
Ease of use
learnability
Intuitiveness
Situational
appropriateness
Definition of Expert Evaluation Criteria
I have developed a final set of gestures based on four evaluation criteria: ease of use, learnability, intuitiveness, and situational appropriateness.

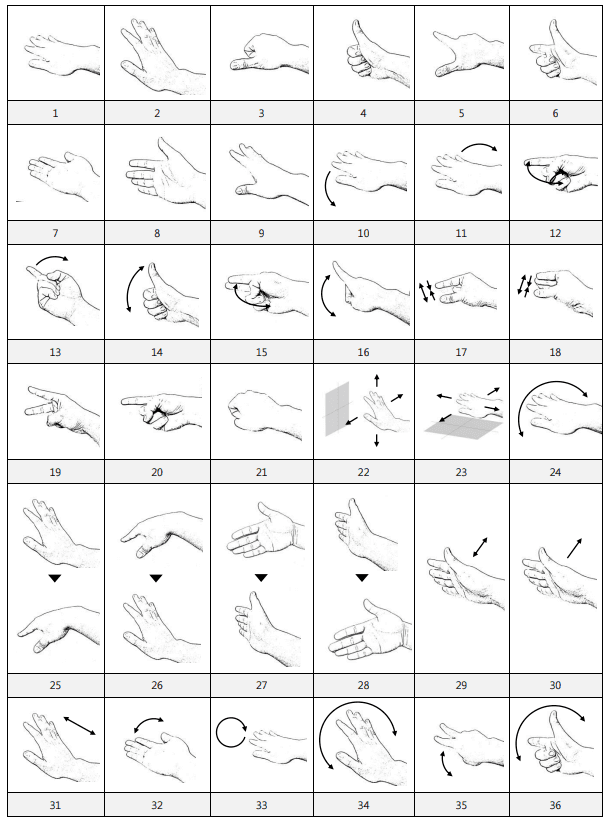
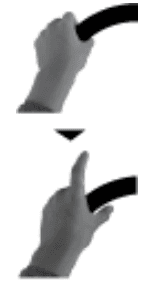
Raising the thumb
and index finger
Gesture command
Description
Gesture command
Description
Gesture command
Description


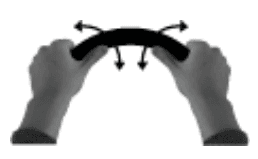

Shaking both
thumbs up and down

Raising the left
thumb and
index finger
Raising the right
thumb and
index finger
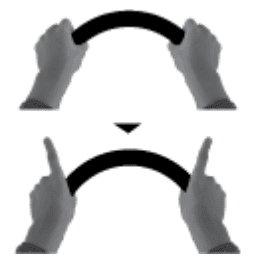
Shaking both
index fingers from
side to side
Shaking the
left index finger
from side to side
Shaking the right
index finger
from side to side
Shaking the left
thumb up and down
Shaking the right
thumb up and down
Lifting both index
fingers
Lifting the left
index finger
Lifting the right
index finger







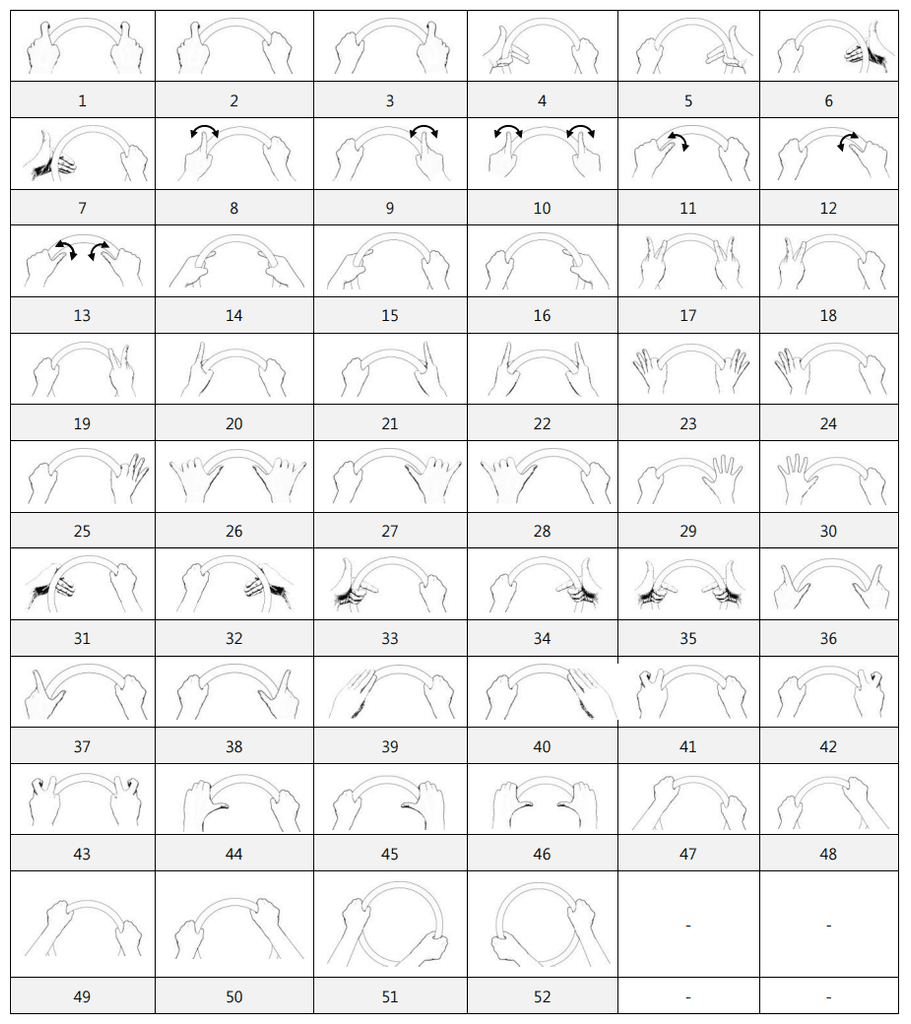
Gesture command
Gesture command
Description
Description


Palming the hand
Placing the hand,
palm down,
in a fixed position
Gesture command
Description
making a fist
Placing the hand
on the palm
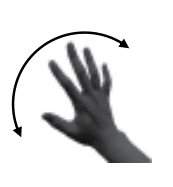
Waving the hand
from side to side
Waving the hand
from side to side
with the palm down
Drawing a circle
with the palm
facing down
Waving the hand
from side to side
with the palm down
Placing the hand
in a fixed position
in space



Clenching the fist
Lowering the hand
from above
Swiping from left
to right.
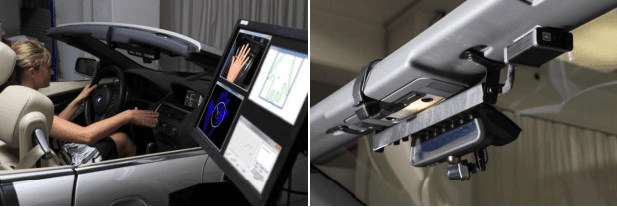
Gesture Design through Expert Group Interviews
I conducted gesture design by mapping the final set of gestures selected for Wheel Gesture and One Hand Gesture to the driver's function manipulation process in the vehicle.
The expert group consisted of six members, including automotive professionals with over 5 years of practical experience in driving medium-sized vehicles (1 male and 1 female),
two UX experts with over 2 years of practical experience (1 male and 1 female), and two master's students majoring in UX design (1 male and 1 female).
All experts had prior experience with gestures on Kinect, Wii, mobile phones, and tablet PCs.
Temperature
Increase
Temperature
Decrease
Intensity Increase
Intensity Decrease
Function
selection gesture
Gesture for adjusting values of the selected function
Function selection gesture for Off
OFF gesture







Function selection
Function selection
Off

음량 감소
Gesture for adjusting values of the selected function
Function
selection gesture
Function selection gesture for Off
OFF gesture
Channel increase
Channel decrease
Volume Increase
Volume Decrease






Function selection
Function selection
Off
Example) Adjusting the heater or air conditioner
Various gesture designs have been developed for heater and air conditioner control.
Fixing a gesture in a specific location to select a function can be beneficial (requires AUI feedback).
Common hand movements horizontally and vertically are convenient for adjusting numerical values.
Example) Adjusting the radio or audio
Various gesture designs have been developed for radio and audio control.
Among the gestures that can be most conveniently and effectively utilized for skipping functions, the index raise is simple and convenient.
A mental model in which left indicates decrease and right indicates increase is intuitive for drivers.
Research Conclusion
Current research in gesture interaction, particularly in the automotive industry, mainly concentrates on non-driving functions
because of technical limitations and safety considerations. However, it is anticipated that,
as technology advances, gesture control will gradually encompass driving-related information and multimedia controls.
Key findings include:
1. Gesture interaction in cars can bring a fresh, emotional experience compared to traditional button controls.
2. For Wheel Gestures, simple gestures using the thumb or index finger were favored, minimizing interference with steering.
3. One Hand Space Gestures, influenced by users' familiarity with existing device interactions, showed a preference for four-directional gestures (up, down, left, right).
Future research should include user evaluations of the final gesture designs and consider diverse driver demographics and driving situations.
Additionally, exploring feedback methods, such as sound cues, is crucial, as these gestures don't rely on screen-based interactions.
The study of efficient combinations of visual, auditory, and tactile feedback in human-to-human interaction is also important for creating natural communication environments.



Copyright © 2025 Min Suk Kang. All rights reserved.

